44
"Trauersinfonie"
e minor
Sinfonien um 1770-1774
Herausgeber: Andreas Friesenhagen und Ulrich Wilker; Reihe I, Band 5b; 2013, G. Henle Verlag München
Symphony No. 44 in E minor
This famous symphony makes clear why Haydn's minor-mode 'Sturm und Drang' works have been so highly regarded. The entire work is terse and concentrated not a note is wasted and sustains its mood of stern passion with remarkable consistency. The only relief from E minor is the bright parallel mode, E major, in the trio of the minuet and the slow movement. In all these respects it bears comparison with Beethoven's second 'Razumovsky' String Quartet.
The symphony is also unusual in that the minuet precedes the slow movement; this pattern is found in only five other Haydn symphonies, all but one of them early. On the other hand it was his invariable pattern in the String Quartets, opp. 9 and 17, as well as three each in Opp. 20 and 33. In any case, the succession of movements here exhibits a combination of expressive force, momentum, and balance among the parts that is exceptional even in Haydn's music.
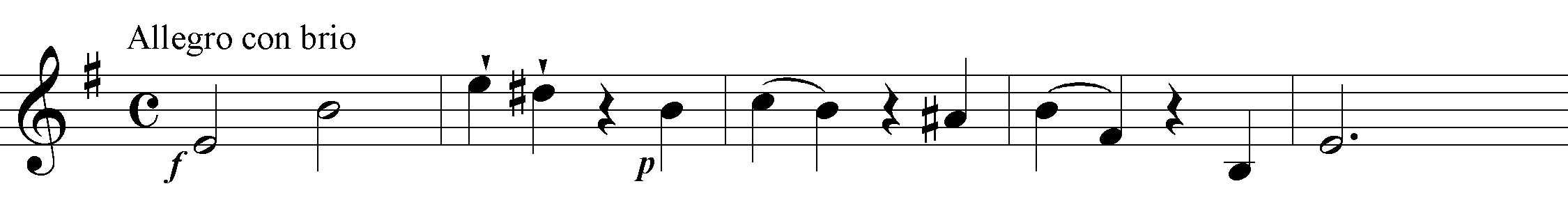
The Allegro con brio is a masterpiece of construction and rhetoric. The stern opening motive, rising in bare octaves through a fifth and a fourth, 1-5-8, is unforgettable. Notwithstanding various contrasting phrases and accompanimental figures, it seems to dominate the entire movement, in a manner reminiscent of the famous 'Quinten' ('Fifths') String Quartet, op. 76 no. 2, also in the minor. In the second group the motive appears several times: at the beginning, in the bass; a few bars later, rising dramatically through three octaves; and still later, in a new harmonic orientation. Towards the very end of the movement, following a pause on a diminished-seventh chord, it returns in three-part imitation, piano, thus producing a climax of suppressed intensity. The most important other idea, a sequential pattern of alternating semiquavers and quavers, is introduced as a countersubject over that bass entry at the beginning of the second group.
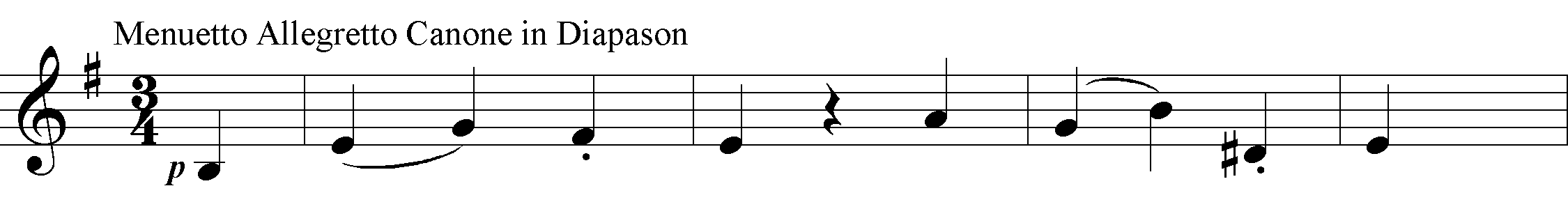
The contrapuntal implications of this movement are (as it were) realized in the minuet, a canon at the octave between melody and bass ('Canone in Diapason'). The violins and first oboe share the melody, while the second oboe and violas double the outer parts freely in thirds, and the horns fill out the harmony (often with motivic significance). The canon is manipulated resourcefully; particularly effective is the passage that in a normal minuet would have been the reprise of the main theme: after a pause, the temporal distance between melody and bass increases from one bar to two, heightening the ominous, troubled air that the spareness and strictness have engendered from the start. Thus the contrast of the Trio is overwhelming, as the violins descend from the heights in radiant E major, and the horns answer by ascending right back.
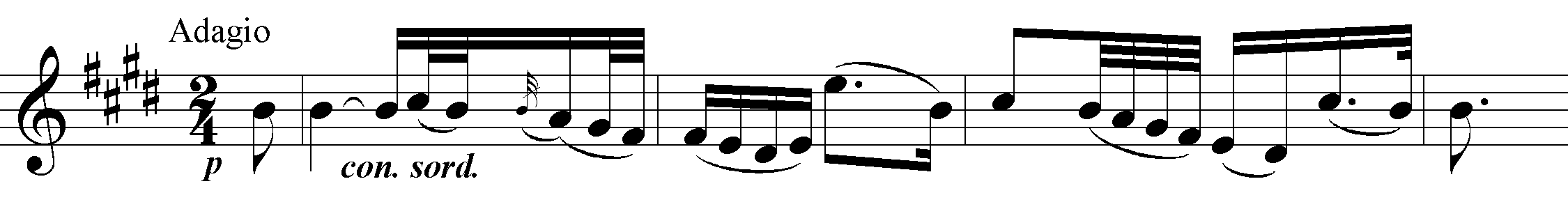
The same minor-major contrast is played out on a larger scale when the repeat of the minuet is followed by the Adagio, again in E major. There is little 'sprightliness' (save in the counter-statement of the opening theme); the mood is solemn and the music unfailingly gorgeous (note, in the second phrase, the upward leap of a tenth rather than an octave). And when the oboes and horns suddenly enter at the end of that counter-statement, we are in the presence of unalloyed beauty and sentiment. As in so many 'Sturm und Drang' symphony slow movements, Haydn takes his time; perhaps in part for this reason he begins the recapitulation directly with that magical oboe/horn entry, even higher than before.
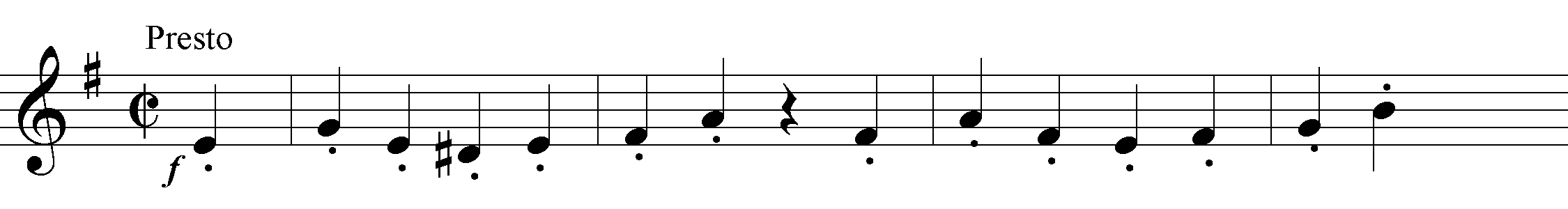
The Finale, Presto alla breve, tops even the Allegro in concentration and drive; Haydn never surpassed the relentless momentum of this movement. Like the Allegro, it begins with a unison theme; as the accompanimental figures accumulate, however, the texture becomes increasingly contrapuntal, until the second group erupts in a double canon (the most virtuosic contrapuntal display in the symphony). Even when homophonic texture is restored, the instability remains at high pitch. Still more thrilling is the development: the head-motive drives through a rising sequence of nine steps, almost 'to the crack of doom' (as Tovey, again, said about Beethoven); from there, a new version of the sequence modulates down almost as many steps, to the home dominant and the retransition. As in the Adagio, Haydn cuts directly to the second group (with the double canon). In this finale, however, a substantial coda returns to the main theme, first in threatening fragments, finally in a climactic cadential version in the bass.
The spurious nickname 'Mourning' arose in the nineteenth century, perhaps owing to a performance of the Adagio during a memorial service for Haydn in Berlin in September 1809. The notion that he wished it to be played at his own funeral seems to be pure legend.
Analysis

Analysis of the movements
Musicians

Musicians
Due to the unclear time of origin of most of Haydn’s symphonies - and unlike his 13 Italian operas, where we really know the exact dates of premieres and performances - detailed and correct name lists of the orchestral musicians cannot be given. As a rough outline, his symphony works can be divided into three temporal blocks. In the first block, in the service of Count Morzin (1757-1761), in the second block, the one at the court of the Esterházys (1761-1790 but with the last symphony for the Esterház audience in 1781) and the third block, the one after Esterház (1782-1795), i.e. in Paris and London. Just for this middle block at the court of the Esterházys 1761-1781 (the last composed symphony for the Esterház audience) respectively 1790, at the end of his service at the court of Esterház we can choose Haydn’s most important musicians and “long-serving companions” and thereby extract an "all-time - all-stars orchestra".
| Flute | Franz Sigl 1761-1773 |
| Flute | Zacharias Hirsch 1777-1790 |
| Oboe | Michael Kapfer 1761-1769 |
| Oboe | Georg Kapfer 1761-1770 |
| Oboe | Anton Mayer 1782-1790 |
| Oboe | Joseph Czerwenka 1784-1790 |
| Bassoon | Johann Hinterberger 1761-1777 |
| Bassoon | Franz Czerwenka 1784-1790 |
| Bassoon | Joseph Steiner 1781-1790 |
| Horn (played violin) | Franz Pauer 1770-1790 |
| Horn (played violin) | Joseph Oliva 1770-1790 |
| Timpani or Bassoon | Caspar Peczival 1773-1790 |
| Violin | Luigi Tomasini 1761-1790 |
| Violin (leader 2. Vl) | Johann Tost 1783-1788 |
| Violin | Joseph Purgsteiner 1766-1790 |
| Violin | Joseph Dietzl 1766-1790 |
| Violin | Vito Ungricht 1777-1790 |
| Violin (most Viola) | Christian Specht 1777-1790 |
| Cello | Anton Kraft 1779-1790 |
| Violone | Carl Schieringer 1768-1790 |
Medias

Music
Antal Dorati
Joseph Haydn
The Symphonies
Philharmonia Hungarica
33 CDs, aufgenommen 1970 bis 1974, herausgegeben 1996 Decca (Universal)





