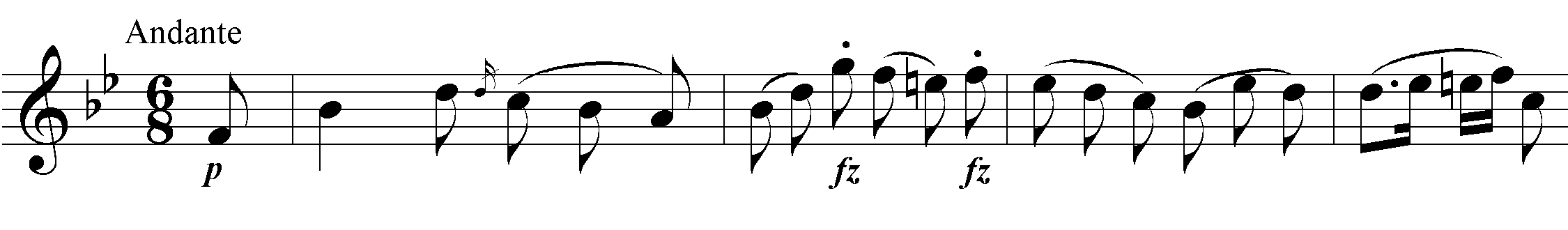84
E flat major
Pariser Sinfonien, 2. Folge
Herausgeber: Sonja Gerlach und Klaus Lippe; Reihe I, Band 13; G. Henle Verlag München
Symphonies Hob.I:82-87
Since the late 1760’s Haydn was no longer an unknown in Paris. Paris was one of the cities in which his instrumental works were regularly performed. Many of Haydn’s symphonies were published at Paris printing houses on into the middle of the 1780’s. In 1784 the newly established Paris Concerts de la Loge Olympique commissioned the composer, who was staying at faraway Eszterháza, to write six grand symphonies for its concert events. The so-called Paris Symphonies (Nos. 82-87), which Joseph Haydn wrote in 1785-86 at the request of the organiser of the Paris Concerts de la Loge Olympique, Comte D’Ogny, are the first sequence of symphonies explicitly designed as a cycle after the Esterhàzy symphonies for the “times of the day” (Matin, Midi, Soir) in 1761 and also represent an important chapter in Haydn’s ascent to European calibre: apart from symphonies 76-78 of 1782, which were envisioned for a trip to England that never came to fruition, the Paris Symphonies are the first which Haydn did not compose for the Esterházy Orchestra. If at Eszterháza Haydn had an average of 22 musicians available to him including 15 or 16 strings, the Paris orchestra had more than 40 violins, ten contrabasses and four times the number of wind instruments, thus an orchestral size likely available to every theatre or orchestral concert organiser today. Only a reference can be made here to the Haydn Academy’s considerations in this regard, which are found in another place of this programme booklet. In terms of style the Paris Symphonies also mark a qualitative leap in Haydn’s symphonic body of work. Haydn could now assert himself in an “international arena.” The secular and extroverted quality of this cycle of works, which embodies the still intact world of the French court – it is the world of Marie Antoinette – is probably attributed to this. The date of the handwritten manuscript shows that No. 83, No. 87 and probably also No. 85 were composed in 1785, No. 82, No. 84 and No. 86, however, in 1786. The sequence of “official” numbering attributed to the first Vienna edition (Wiener Erstausgabe, Artaria 1887) and adopted by the old complete edition (Alte Gesamtausgabe) and Hoboken catalogue (Hoboken Verzeichnis) was not the one Haydn had originally intended. In Haydn’s letter (composed in his incomparable orthography) to the Viennese publishing house Artaria dated 2 August 1787, after he had sent the manuscripts to the publisher, he explicitly called the publisher’s attention to the correct sequence – which the publisher then failed to follow: “Last time I forgot to indicate the order of the symphonies, which should be engraved as follows: Symphony in A No. 1, in B Flat No. 2, in G [minor] No. 3, in E-Flat No. 4, in D No. 5 in C No. 6,” or translated in the numbering commonly used: Nos. 87, 85, 83, 84, 86, 82. Three of the Paris Symphonies received sobriquets that have stuck: No. 82, L’Ours, No. 83, La Poule and No. 85, La Reine de France. As a more or less direct result of the initial commission, the subsequent five symphonies (Nos. 88-92) were originally intended for Paris as well. Nos. 88 and 89 were composed in 1787 and are among the works Joseph Haydn gave the Esterházy violinist Johann Tost on his journey to Paris so he could make a name for himself there, but also very likely because Haydn wanted to keep the interest of the Parisians in his compositions alive after the Paris Symphonies (Nos. 82.87). Nos. 90-91were written by Haydn in 1788/89 at the behest of the Loge Olympique in Paris basically as a follow-up to the six Paris Symphonies Nos. 82-87 and are dedicated to the original client, the Comte d’Ogny. At the same time, Haydn, a competent businessman, had also sold these symphonies to Prince Oettingen-Wallerstein, a fervent admirer of Haydn who commissioned symphonies from him. (To the question of why the prince only received scores written by a copyist Haydn explained that an eye condition had prevented him from delivering it in his own script.) No. 92, the famous Oxford Symphony, was originally composed in the scope of this commission, then apparently completed too late. Haydn then used it in 1792 for the celebration for the conferring of his honorary doctorate in Oxford and in this way it forms the direct link to the subsequent London Symphonies (Nos. 93-104), which represent the crowning conclusion of Haydn’s body of symphonic work.
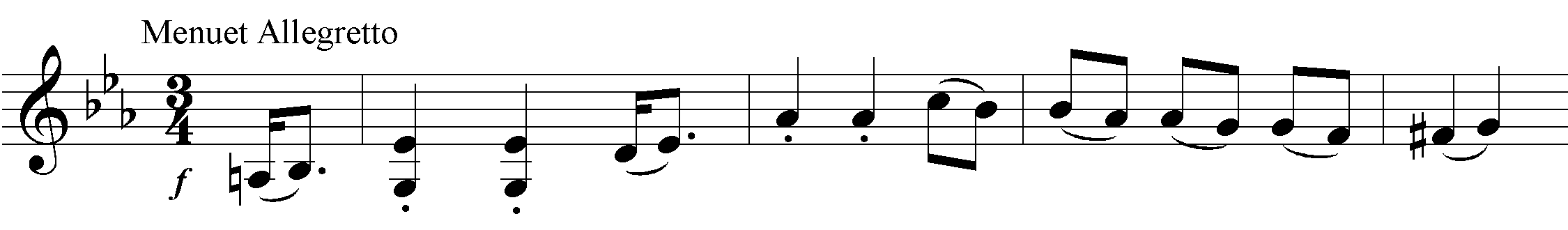
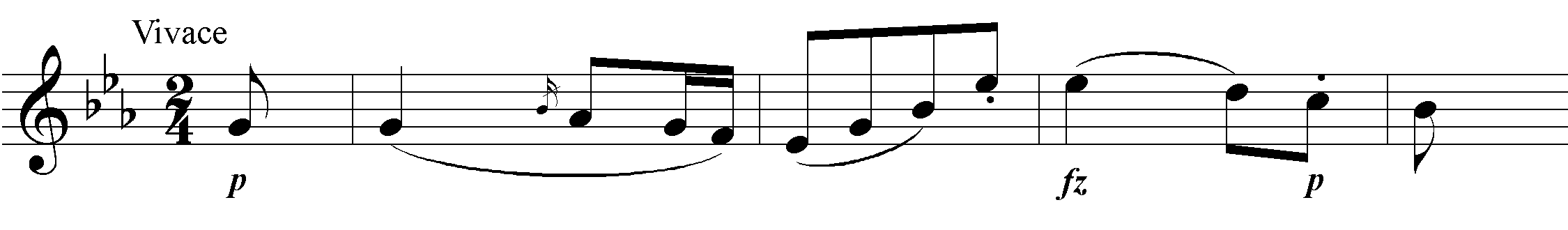
Hob.I:84 Symphony in E-Flat Major
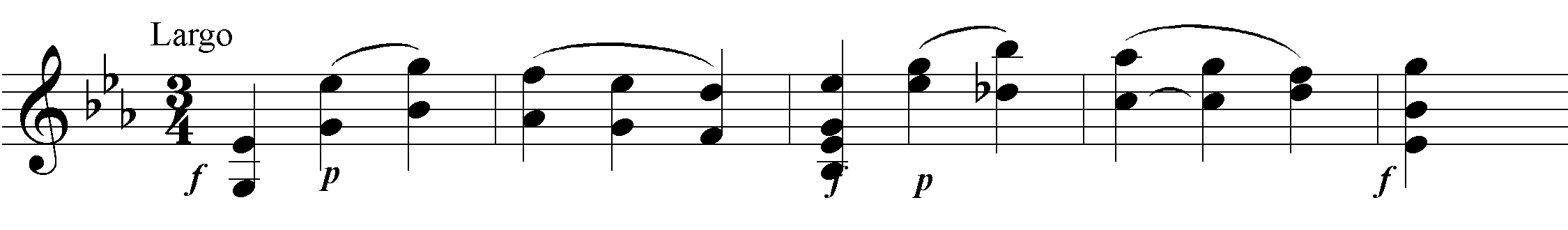
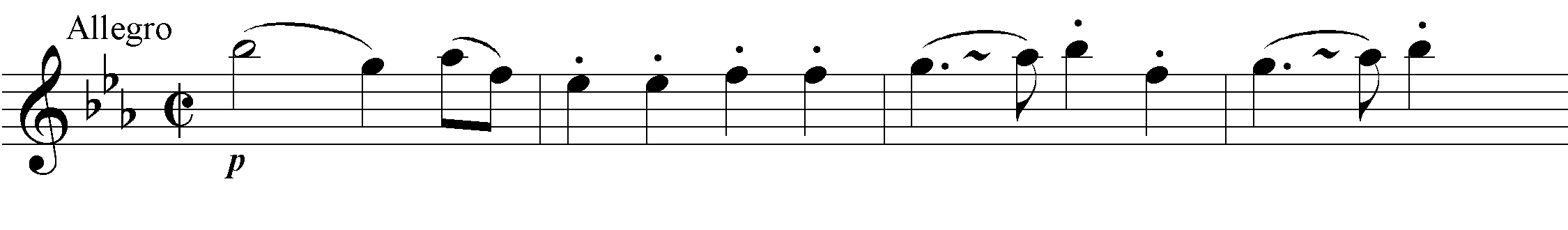
According to the date on the handwritten score, Symphony No. 84 was the second to last symphony completed in 1786, before No. 86, and was originally intended by Joseph Haydn himself to be the fourth in the cycle. The sobriquet Les sept paroles, which this symphony acquired from a French author in the late 19th century, is probably due to a mix-up with the “instrumental music for the Seven Words of Our Saviour on the Cross” of the same year, 1785, but is definitely inauthentic and incongruous. On the contrary: there is probably no other work of Haydn for which such a sobriquet could be less fitting. Despite its slow introduction, the first movement is unmistakeably secular in tone. It is a monothematic sonata movement: a variant of the principal theme serves as the secondary theme. The second movement is a movement of variations: in the variations, the first of which immediately falls into the B minor variant, Haydn unfurls his celebrated instrumentational artistry. In the coda the theme reappears in stretto. The minuet is basically a typical representative of that genre which no other composer conceived of in as rich and varied a fashion as Haydn. The boundaries between rural lightheartedness and “courtly noblesse” are effortlessly blurred to create just as great of an “entertainment value” as with a “consummate” first or last movement of a symphony. The finale is again a monothematic sonata movement in which a musical cosmos dotted with counterpoint and chromaticisms is magically produced out of a folksong-like principal theme in a virtuosic and brilliant way.
Analysis

Analysis of the movements
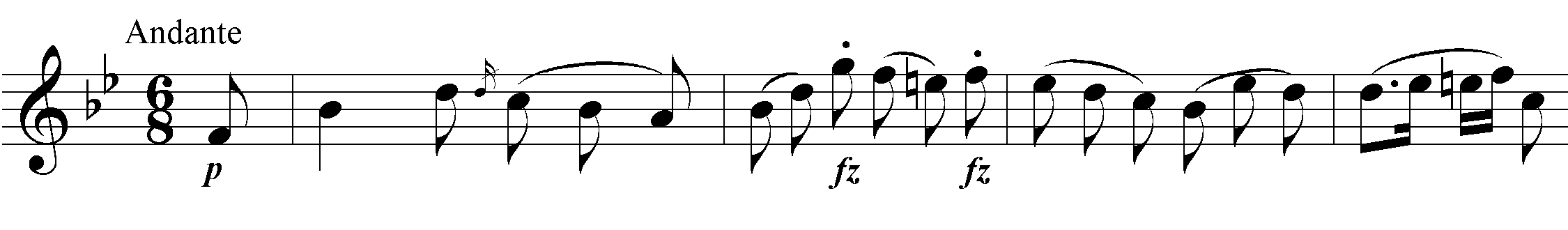
Musicians

Musicians
Due to the unclear time of origin of most of Haydn’s symphonies - and unlike his 13 Italian operas, where we really know the exact dates of premieres and performances - detailed and correct name lists of the orchestral musicians cannot be given. As a rough outline, his symphony works can be divided into three temporal blocks. In the first block, in the service of Count Morzin (1757-1761), in the second block, the one at the court of the Esterházys (1761-1790 but with the last symphony for the Esterház audience in 1781) and the third block, the one after Esterház (1782-1795), i.e. in Paris and London. Just for this middle block at the court of the Esterházys 1761-1781 (the last composed symphony for the Esterház audience) respectively 1790, at the end of his service at the court of Esterház we can choose Haydn’s most important musicians and “long-serving companions” and thereby extract an "all-time - all-stars orchestra".
| Flute | Franz Sigl 1761-1773 |
| Flute | Zacharias Hirsch 1777-1790 |
| Oboe | Michael Kapfer 1761-1769 |
| Oboe | Georg Kapfer 1761-1770 |
| Oboe | Anton Mayer 1782-1790 |
| Oboe | Joseph Czerwenka 1784-1790 |
| Bassoon | Johann Hinterberger 1761-1777 |
| Bassoon | Franz Czerwenka 1784-1790 |
| Bassoon | Joseph Steiner 1781-1790 |
| Horn (played violin) | Franz Pauer 1770-1790 |
| Horn (played violin) | Joseph Oliva 1770-1790 |
| Timpani or Bassoon | Caspar Peczival 1773-1790 |
| Violin | Luigi Tomasini 1761-1790 |
| Violin (leader 2. Vl) | Johann Tost 1783-1788 |
| Violin | Joseph Purgsteiner 1766-1790 |
| Violin | Joseph Dietzl 1766-1790 |
| Violin | Vito Ungricht 1777-1790 |
| Violin (most Viola) | Christian Specht 1777-1790 |
| Cello | Anton Kraft 1779-1790 |
| Violone | Carl Schieringer 1768-1790 |
Medias

Music
Antal Dorati
Joseph Haydn
The Symphonies
Philharmonia Hungarica
33 CDs, aufgenommen 1970 bis 1974, herausgegeben 1996 Decca (Universal)