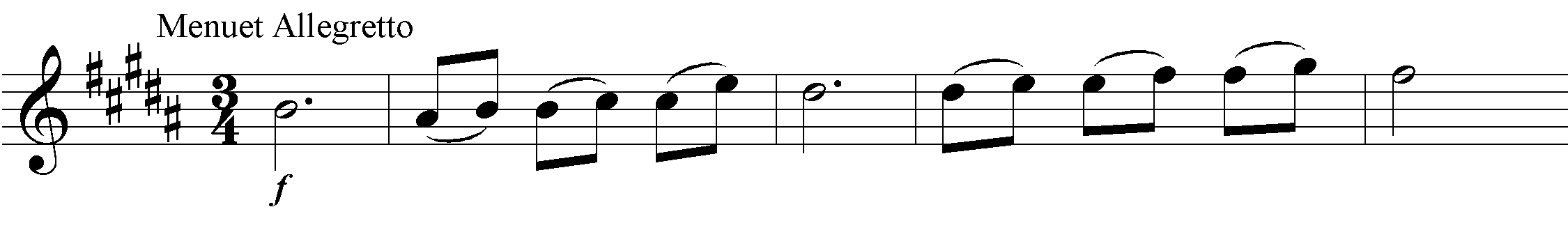46
B major
Sinfonien 1767-1772
Herausgeber: Carl-Gabriel Stellan Mörner; Reihe I, Band 6; G. Henle Verlag München
Symphony No. 46 in B major
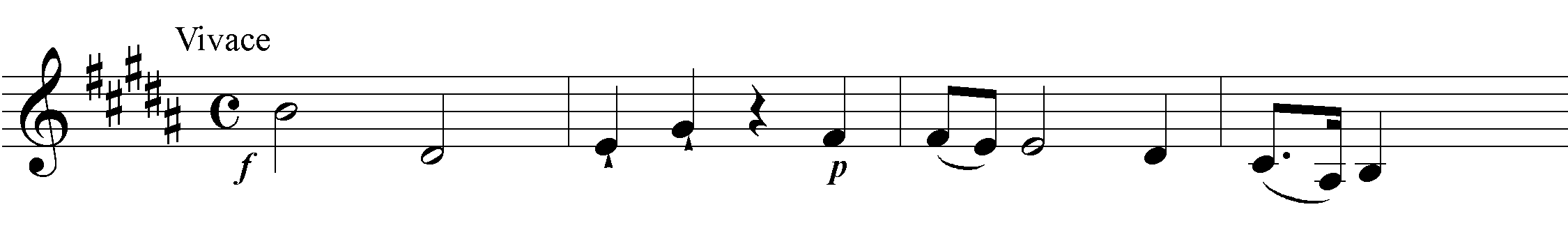
This symphony is in many ways a pair to the 'Farewell'. It too is set in an unusual, 'remote' sharp-side key; more fundamentally, it too disrupts symphonic conventions. After a complex opening Vivace, a conspiratorial siciliano Poco adagio in B minor, and a galant minuet, the Presto finale breaks off towards the end for a long reprise of the minuet, and then resumes and concludes.
The minuet begins as a vigorous forte, and continues so after the double bar; but the reprise as so often in Haydn minuets is varied. The winds drop out, and the dynamics shift to piano; the initial quarter-rest in the bass is expanded to more than a measure, during which silence the opening phrase returns in a free retrograde: a 'dying fall'. Furthermore, this reprise stands on the dominant; it thus creates a progressive, non-symmetrical form for the minuet as a whole. The trio, in B minor, invokes an 'exotic' aura by means of non-functional progressions, a heaping-up of harmonic, instrumental, and dynamic surprises, and ambiguous tonality.
Outwardly, the finale is typical of the period. However, the beginning is 'weak': it is scored for violins alone and projects the tonic triad in first inversion (over D sharp) rather than in root position. It is also rhythmically unsettled, and unusually quiet for a finale-theme; presumably, these features are among those signaled by the heading 'scherzando'. The very short development centres around the dominant of the relative minor, and the mediant, both also built on D sharp. And the recapitulation breaks off, again on the dominant, before reaching the structural cadence.
Thus it is consequential that the recall of the minuet also begins on the dominant, with the internal reprise; its opening section is never heard. A deceptive cadence leads quickly to a newly unstable dominant and a fermata; suddenly the Presto head-motive bursts in, harmonized by a forte root-position VI cadence the first and only such conjunction in the movement. There follows the 'missing' ending of the recapitulation, dying-away on the tag-motive (repeated in augmentation). Hence the coda, with its pedal in the low horns, is not merely a good joke in 'scherzando' style; it also provides the minimum satisfactory degree of tonal confirmation.
Why does Haydn recall the minuet in the finale, and fuse these two movements into a through-composed complex? The melodic material of the minuet is based largely on a two-note appoggiatura figure; that is, a 'sighing' motive. In the reprise, however, the sighs come to the fore, creating the aforementioned 'dying fall'. Now in the minuet this passage is already a varied reprise. Hence in the finale, the minuet-recall is a 'second-order' reprise, music 'about' a reprise; its content is not a reprise in the usual sense, but the experience of hearing a reprise. In addition, the minuet-reprise is generically shocking, unforeseeable; as it begins, we don't know what is happening; it takes a moment to get our bearings. It is thus not merely a recall, but a reminiscence; a re-experiencing, tinged with nostalgia or regret, which incorporates its own past into its sounding present.
Furthermore, this meta-musical reminiscence does not belong to the world of ordinary symphonic discourse. The minuet recall is 'framed', by the gesture of breaking off, by the differences in style, by its self-reflexive nature. And what is thus framed? A dying fall, which we have heard before but at first cannot quite place, which seems to say, 'Once upon a time there was a happier world, a world of ordered minuets, unlike this hurlyburly', and to say this in a tone of nostalgia and regret.
Hence the underlying idea of Symphony No. 46 must lie in its manifold relationships with the 'Farewell' Symphony. In what order did Haydn intend these two extraordinary works to be heard? (There is no documentary evidence.) Did the B major work come last? Do its slightly more familiar key and major mode invoke life back in Eisenstadt, with the joking finale suggesting that 'they all lived happily ever after'? Or did it come first? Is it an image of life at Eszterhäza (minor mode; Balkanisms), the bittersweet minuet-reminiscence a reminder of happy, ordered times in Eisenstadt, not yet regained, which in the 'Farewell' will progress through unbearable tension to a vision of longing? Scholars cannot answer these questions; but there is no reason why listeners should not enjoy speculating on them.
Analysis

Analysis of the movements

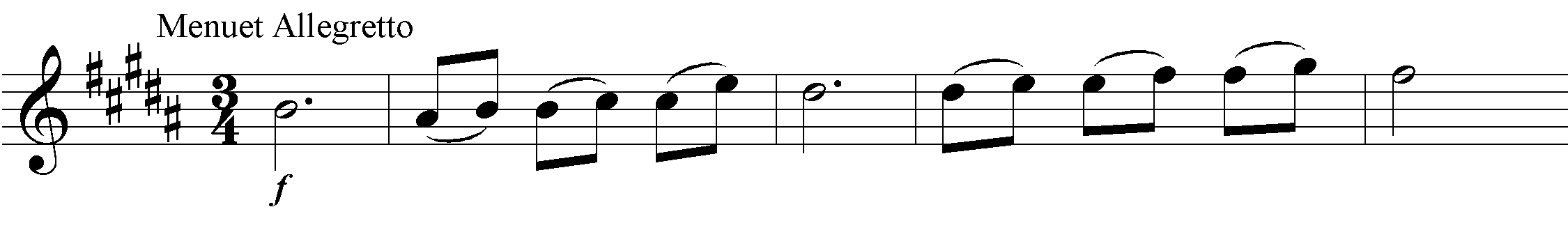

Musicians

Musicians
Due to the unclear time of origin of most of Haydn’s symphonies - and unlike his 13 Italian operas, where we really know the exact dates of premieres and performances - detailed and correct name lists of the orchestral musicians cannot be given. As a rough outline, his symphony works can be divided into three temporal blocks. In the first block, in the service of Count Morzin (1757-1761), in the second block, the one at the court of the Esterházys (1761-1790 but with the last symphony for the Esterház audience in 1781) and the third block, the one after Esterház (1782-1795), i.e. in Paris and London. Just for this middle block at the court of the Esterházys 1761-1781 (the last composed symphony for the Esterház audience) respectively 1790, at the end of his service at the court of Esterház we can choose Haydn’s most important musicians and “long-serving companions” and thereby extract an "all-time - all-stars orchestra".
| Flute | Franz Sigl 1761-1773 |
| Flute | Zacharias Hirsch 1777-1790 |
| Oboe | Michael Kapfer 1761-1769 |
| Oboe | Georg Kapfer 1761-1770 |
| Oboe | Anton Mayer 1782-1790 |
| Oboe | Joseph Czerwenka 1784-1790 |
| Bassoon | Johann Hinterberger 1761-1777 |
| Bassoon | Franz Czerwenka 1784-1790 |
| Bassoon | Joseph Steiner 1781-1790 |
| Horn (played violin) | Franz Pauer 1770-1790 |
| Horn (played violin) | Joseph Oliva 1770-1790 |
| Timpani or Bassoon | Caspar Peczival 1773-1790 |
| Violin | Luigi Tomasini 1761-1790 |
| Violin (leader 2. Vl) | Johann Tost 1783-1788 |
| Violin | Joseph Purgsteiner 1766-1790 |
| Violin | Joseph Dietzl 1766-1790 |
| Violin | Vito Ungricht 1777-1790 |
| Violin (most Viola) | Christian Specht 1777-1790 |
| Cello | Anton Kraft 1779-1790 |
| Violone | Carl Schieringer 1768-1790 |
Medias

Music
Antal Dorati
Joseph Haydn
The Symphonies
Philharmonia Hungarica
33 CDs, aufgenommen 1970 bis 1974, herausgegeben 1996 Decca (Universal)